Ephrin type-B receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHB4 gene.
Ephrin receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, mediate numerous developmental processes, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. The protein encoded by this gene binds to ephrin-B2 and plays an essential role in vascular development.
References
Further reading

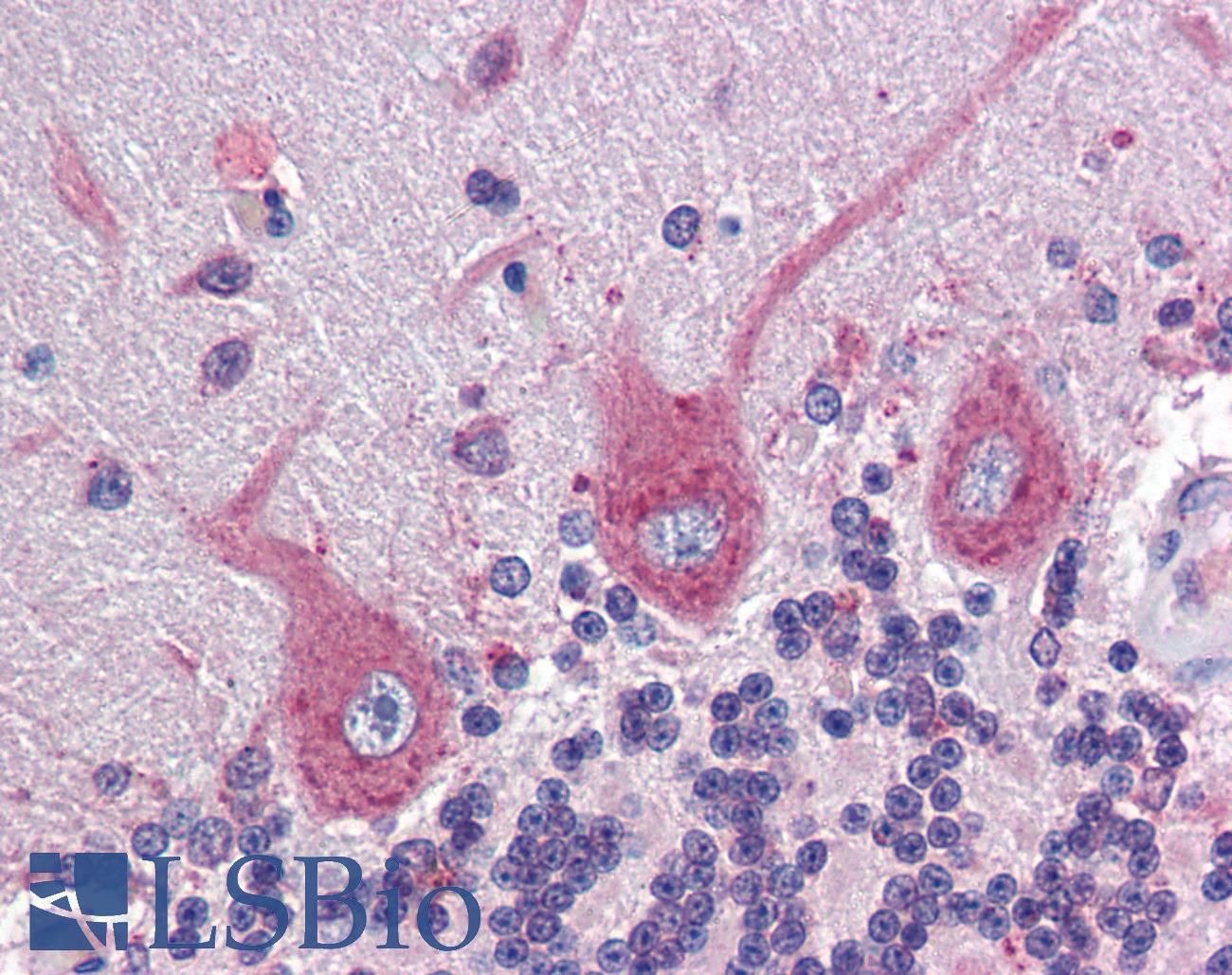

![Eph receptor B4/HTK抗体[04] BSA and Azide free Abcam中文官网](https://www.abcam.cn/ps/products/277/ab277130/Images/ab277130-2-AntiEph-receptor-B4HTK-antibody-ICC-MCF7-cells.jpg)