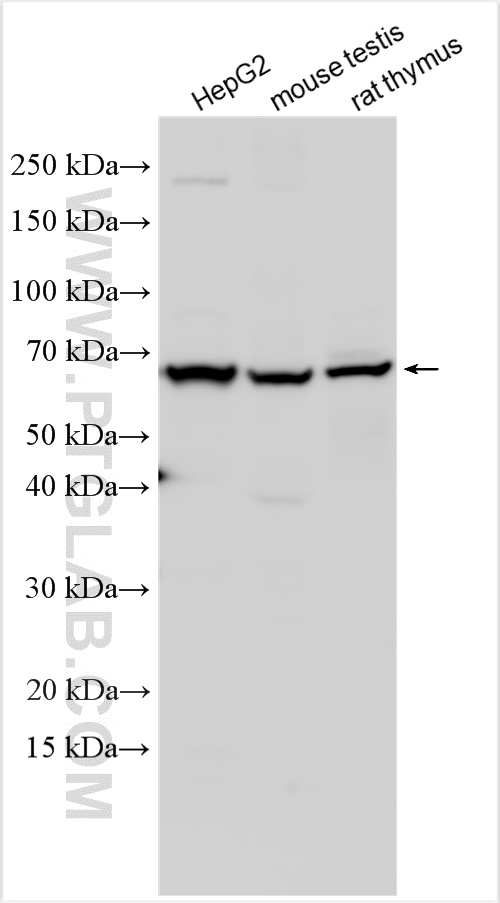
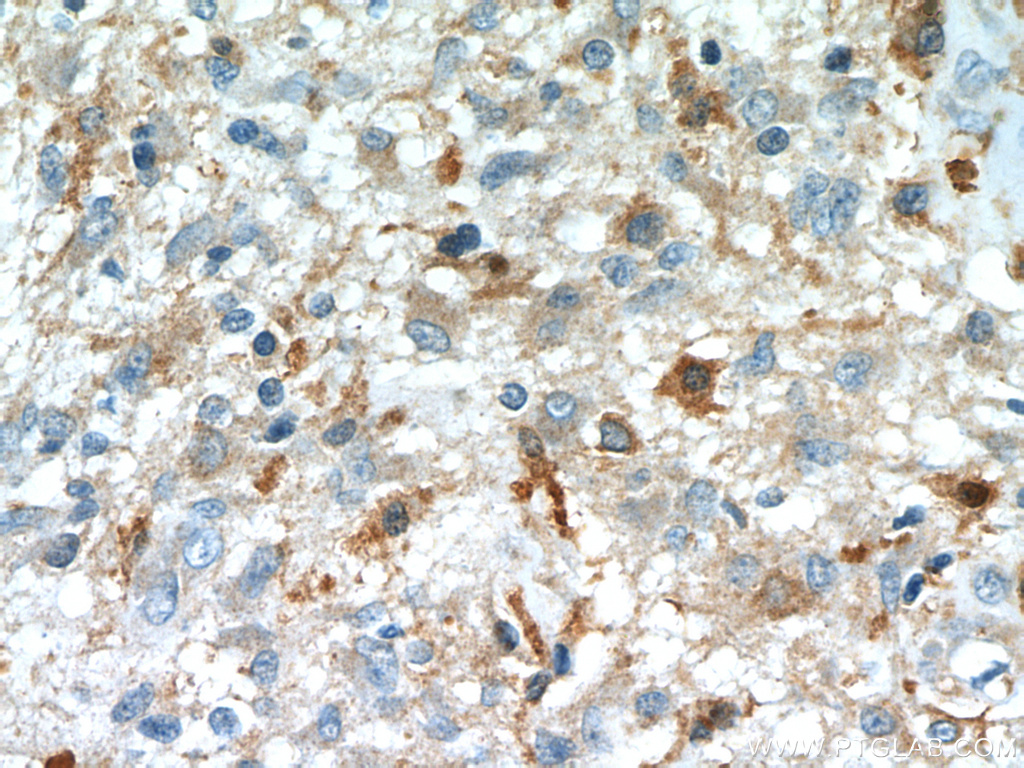
Interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-2 (IL-13Rα2), also known as CD213A2 (cluster of differentiation 213A2), is a membrane bound protein that in humans is encoded by the IL13RA2 gene.
Function
IL-13Rα2 is closely related to IL-13Rα1, a subunit of the interleukin-13 receptor complex. This protein binds IL13 with high affinity, but lacks any significant cytoplasmic domain, and does not appear to function as a signal mediator. It is, however, able to regulate the effects of both IL-13 and IL-4, despite the fact it is unable to bind directly to the latter. It is also reported to play a role in the internalization of IL13.
Clinical Significance
IL-13Rα2 has been found to be over-expressed in a variety of cancers, including pancreatic, ovarian, melanomas, and malignant gliomas.
See also
- Interleukin-13 receptor
References
Further reading
External links
- IL13RA2 protein, human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: Q14627 (Interleukin-13 receptor subunit alpha-2) at the PDBe-KB.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.